
Cream cheese is a popular and versatile ingredient that is commonly used in both sweet and savory dishes. Whether spread on a bagel, used as a dip for fruits or vegetables, or incorporated into a recipe, cream cheese adds a creamy and tangy flavor. However, you may wonder if cream cheese is a healthy choice due to its high fat content.
Despite its high fat content, cream cheese can be a part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. It is important to note that not all fats are created equal, and the type of fat found in cream cheese can have different effects on health. Cream cheese is a rich source of saturated fat, which is known to raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease when consumed in excess. Therefore, it is recommended to limit intake and choose low-fat or reduced-fat options when possible.
On the other hand, cream cheese has some nutritional benefits. It is a good source of calcium, which is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Additionally, cream cheese contains protein, which is important for building and repairing tissues in the body. However, it is worth noting that cream cheese is not a significant source of other essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals.
Overall, while cream cheese can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet, it is important to consume it in moderation due to its high fat content. Choosing low-fat or reduced-fat options can be a healthier alternative. Additionally, pairing cream cheese with nutrient-rich foods, such as whole grain bread or fresh vegetables, can help to improve the overall nutritional value of a meal or snack.
Good source of vitamin A
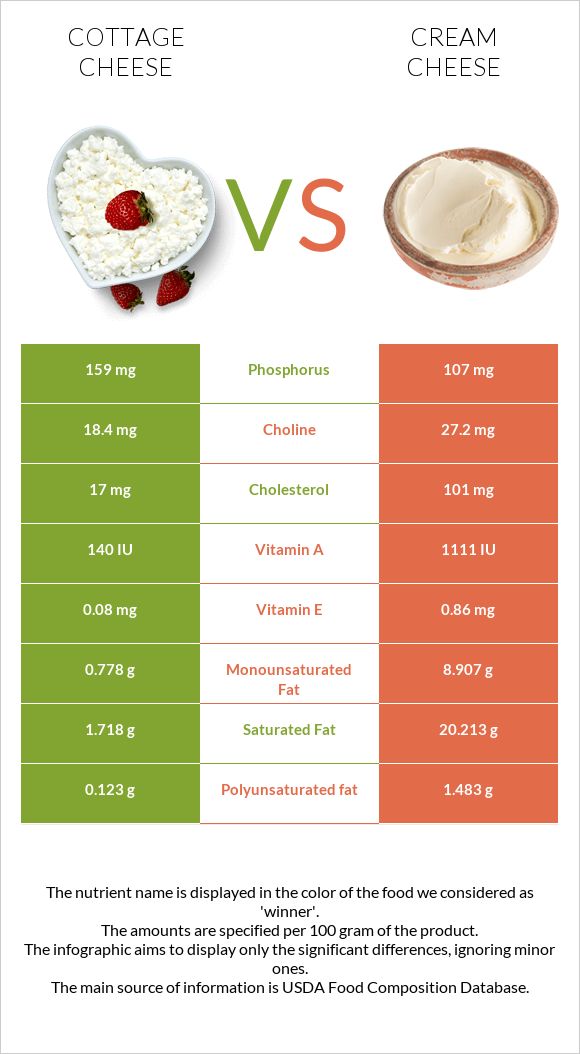
Cream cheese is a good source of vitamin A, which is an essential nutrient for maintaining healthy eyesight and a strong immune system. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
One ounce of cream cheese provides approximately 10% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin A. This vitamin is important for the proper functioning of the retina and can help prevent night blindness and other vision problems. Additionally, vitamin A is necessary for the growth and development of cells, including those in the immune system.
Consuming cream cheese as part of a balanced diet can help you meet your vitamin A needs. However, it’s important to note that cream cheese is also high in saturated fat, so it should be enjoyed in moderation as part of an overall healthy eating plan.
To increase your vitamin A intake, consider pairing cream cheese with foods that are rich in this nutrient, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach. This can help ensure you’re getting a variety of nutrients to support your overall health.
Supplies antioxidants

Antioxidants are compounds that help protect your body against oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals.
Cream cheese contains small amounts of certain antioxidants, such as vitamin A and vitamin E. These antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress in the body.
Vitamin A is known for its role in maintaining healthy vision and supporting immune function. It also acts as an antioxidant, helping to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Vitamin E is another potent antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative damage. It also supports healthy immune function and plays a role in skin health.
While cream cheese does provide some antioxidants, it’s important to note that the levels are relatively low compared to other foods such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
Therefore, while cream cheese can contribute some antioxidants to your diet, it’s still important to consume a variety of antioxidant-rich foods to ensure you’re getting an adequate intake.
May have probiotic effects
Cream cheese may have probiotic effects because it is often made by fermenting milk with lactic acid bacteria, such as Lactobacillus. These bacteria can survive the low pH and high salt concentrations in cream cheese and may have the ability to survive digestion and reach the gut alive.
Probiotics are living microorganisms that have various health benefits when consumed. They are believed to improve gut health by restoring the balance of bacteria in the digestive system. Probiotics may also enhance immune function and reduce the risk of certain diseases, such as diarrhea and irritable bowel syndrome.
While cream cheese may contain probiotics, it’s important to note that not all brands or types of cream cheese contain live and active cultures. Some cream cheese products are pasteurized, which can kill the beneficial bacteria. Therefore, it’s essential to check the label or choose a cream cheese brand that specifically states that it contains live and active cultures.
Additionally, the probiotic content in cream cheese is generally lower compared to other fermented dairy products, such as yogurt or kefir. Therefore, if you’re looking to increase your probiotic intake, it may be more beneficial to choose other dairy products that have a higher concentration of live and active cultures.
Overall, while cream cheese may have probiotic effects, it’s important to consider the specific brand and type you choose, as well as the overall balance of your diet, to ensure you’re consuming a variety of probiotic-rich foods for optimal gut health.
Low in lactose

Cream cheese is considered to be a low-lactose cheese, making it a suitable option for those who are lactose intolerant or have difficulty digesting lactose. Lactose is a natural sugar found in milk and dairy products. It is broken down by an enzyme called lactase, which some individuals do not produce in sufficient amounts.
During the cheese-making process, most of the lactose is removed along with the whey, resulting in a cheese with a lower lactose content. This is because bacteria cultures used in making cream cheese convert lactose into lactic acid. As a result, cream cheese typically contains only trace amounts of lactose, making it easier to digest for those with lactose intolerance.
However, it is important to note that the lactose content can vary between different brands and types of cream cheese. Some manufacturers may add small amounts of cream or milk to enhance the taste or texture, which can increase the lactose content. Read the nutrition labels and ingredient lists to determine the lactose content of a specific cream cheese product.
If you have lactose intolerance or are following a low-lactose diet, you may still be able to enjoy cream cheese in moderation. Many individuals with lactose intolerance can tolerate small amounts of lactose without experiencing discomfort. However, if you have a severe intolerance or sensitivity to lactose, it is recommended to opt for lactose-free or dairy-free cream cheese alternatives.
Low in protein
Cream cheese is relatively low in protein compared to other dairy products. Protein is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting a healthy immune system.
While cream cheese does contain some protein, it is not a significant source compared to other foods like meat, fish, eggs, or legumes. Therefore, if you are looking to increase your protein intake, you may want to consider other options.
It’s important to note that if you rely on cream cheese as a major source of protein, you may not be meeting your daily protein needs. It’s generally recommended to consume a variety of protein-rich foods to ensure an adequate intake.
Short shelf-life

Cream cheese has a relatively short shelf-life compared to some other types of cheeses. Due to its high moisture content and limited preservation methods, cream cheese typically has a shorter expiration date once opened.
It is recommended to consume cream cheese within 1-2 weeks of opening, although this may vary depending on the specific brand and storage conditions. It is important to check the expiration date and storage guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
Additionally, cream cheese should be stored properly in the refrigerator to maintain its quality and safety. It should be kept in an airtight container or wrapped tightly in plastic wrap to prevent contamination and reduce moisture loss. Storing cream cheese in its original packaging can also help extend its shelf-life.
It is worth noting that the texture and flavor of cream cheese may change as it ages, and consuming cream cheese beyond its recommended shelf-life may increase the risk of foodborne illness. Therefore, it is important to be mindful of the expiration date and storage instructions to ensure both safety and optimal taste.
Overall, due to its short shelf-life, it is advisable to purchase and consume cream cheese in small quantities to minimize waste and ensure freshness.








